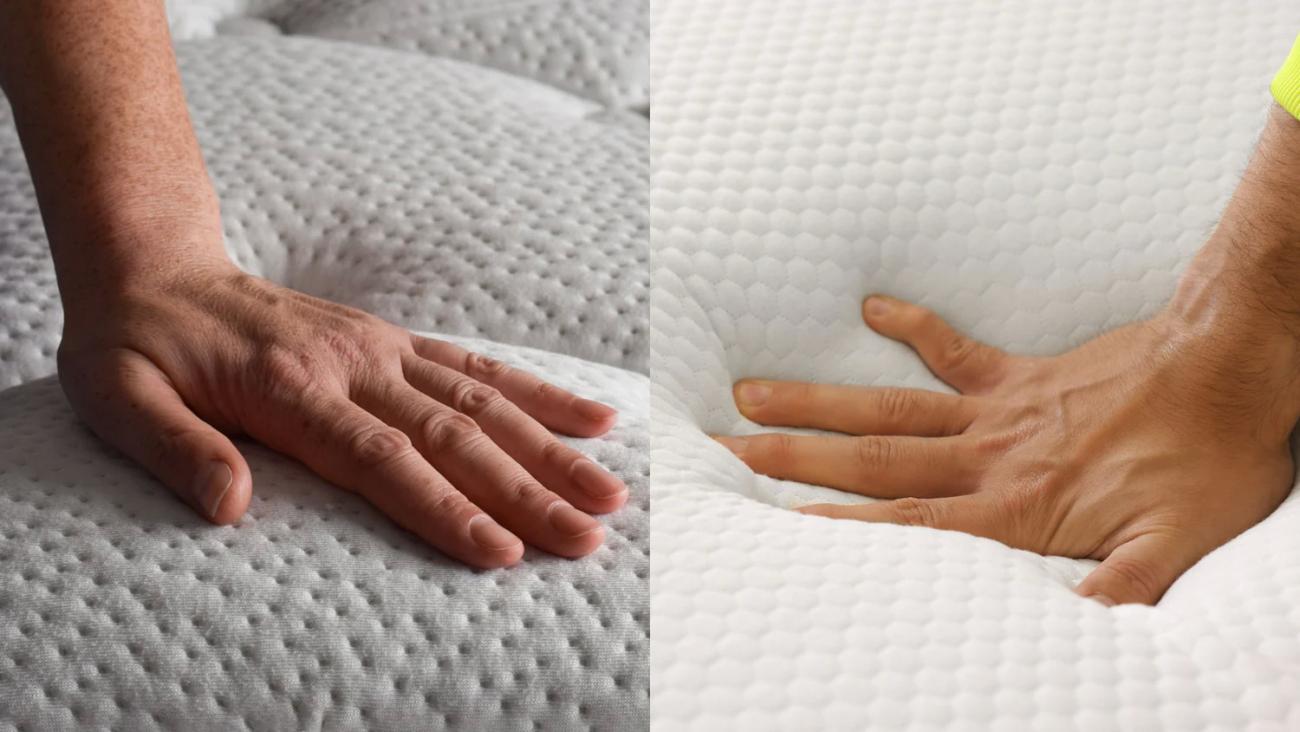
What Is the Mattress Firmness Scale?
The mattress firmness scale is a standardized system that rates mattresses from 1 to 10, with 1 being extra soft and 10 being extra firm. This scale helps you compare different mattresses and make an informed decision based on your body type, sleep position, and preferences.

Why Mattress Firmness Matters
Firmness impacts spinal alignment, pressure relief, and overall comfort. A mattress that’s too soft can cause your body to sink excessively, leading to poor spinal alignment, while an overly firm mattress may create pressure points, leading to discomfort. Finding the right firmness ensures a balance between support and cushioning.
Mattress Firmness by Sleeping Position
Your preferred sleeping position plays a significant role in determining the ideal mattress firmness:

Factors Influencing Firmness Perception
While the firmness scale provides a guide, your experience with a mattress can vary due to:
Preferences for softness or firmness depend on how much cushioning and support you find comfortable.
How to Test Mattress Firmness
In-Store Testing

Sleep Trials
Common Misconceptions About Mattress Firmness
Softness Equals Lack of Support
Modern mattresses can provide both plush comfort and adequate support, especially when made with high-quality materials.
Firmer Is Always Better for Back Pain
While firm mattresses offer support, overly firm surfaces can create pressure points. Medium-firm mattresses are usually the best choice for back pain relief.
Universal Comfort Mattresses Suit Everyone
Comfort is subjective. While some mattresses claim universal appeal, always prioritize your personal needs and preferences.
Mattress Firmness for Couples
Couples often have different firmness preferences. Options like split mattresses or adjustable firmness beds allow each partner to select their desired level of firmness for a customized experience.

Key Takeaways
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right mattress firmness is essential for a good night’s sleep and overall well-being. By understanding the mattress firmness scale and considering your unique needs, you can make an informed decision that improves your sleep quality and supports your health.

The News 14/12/2025
Architectural Digest gợi ý Cloud Dancer phù hợp với plush fabrics và những hình khối “mềm”, tránh cảm giác cứng/rigid; họ liên hệ nó với cảm giác “weightless fullness” (nhẹ nhưng đầy) [3]. Đây là cơ hội cho các dòng vải bọc, rèm, thảm, bedding: màu trắng ngà làm nổi sợi dệt và tạo cảm giác chạm “ấm”.Pantone has announced the PANTONE 11-4201 Cloud Dancer as the Color of the Year 2026: a "buoyant" and balanced white, described as a whisper of peace in the midst of a noisy world. This is also the first time Pantone has chosen a white color since the "Color of the Year" program began in 1999. Pantone calls Cloud Dancer a "lofty/billowy" white tone that has a relaxing feel, giving the mind more space to create and innovate [1].

The News 04/12/2025
The Netherlands is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change, with about a third of its area lying below sea level and the rest regularly at risk of flooding. As sea levels are forecast to continue to rise and extreme rains increase, the government is not only strengthening dikes and tidal culverts, but also testing new adaptation models. Floating housing in Amsterdam – typically the Waterbuurt and Schoonschip districts – is seen as "urban laboratories" for a new way of living: not only fighting floods, but actively living with water. In parallel with climate pressures, Amsterdam faces a shortage of housing and scarce land funds. The expansion of the city to the water helps solve two problems at the same time: increasing the supply of housing without encroaching on more land, and at the same time testing an urban model that is able to adapt to flooding and sea level rise.

The News 20/11/2025
Kampung Admiralty - the project that won the "Building of the Year 2018" award at the World Architecture Festival - is a clear demonstration of smart tropical green architecture. With a three-storey "club sandwich" design, a natural ventilation system that saves 13% of cooling energy, and a 125% greening rate, this project opens up many valuable lessons for Vietnamese urban projects in the context of climate change.

The News 10/11/2025
In the midst of the hustle and bustle of urban life, many Vietnamese families are looking for a different living space – where they can enjoy modernity without being far from nature. Tropical Modern villa architecture is the perfect answer to this need. Not only an aesthetic trend, this is also a smart design philosophy, harmoniously combining technology, local materials and Vietnam's typical tropical climate.

The News 25/10/2025
Hemp-lime (hempcrete) is a non-load-bearing covering material consisting of a hemp wood core (hemp shiv/hurd) combined with a lime-based adhesive, outstanding for its insulation – moisture conditioning – indoor environmental durability; in particular, IRC 2024 – Appendix BL has established a normative line applicable to low-rise housing, strengthening the technical-legal feasibility of this biomaterial.

The News 11/10/2025
Amid rapid urbanization and global climate change, architecture is not only construction but also the art of harmonizing people, the environment, and technology. The Bahrain World Trade Center (BWTC)—the iconic twin towers in Manama, Bahrain—is a vivid testament to this fusion. Completed in 2008, BWTC is not only the tallest building in Bahrain (240 meters) but also the first building in the world to integrate wind turbines into its primary structure, supplying renewable energy to itself [1]. This article explores the BWTC’s structural system and design principles, examining how it overcomes the challenges of a desert environment to become a convincing sustainable model for future cities. Through an academic lens, we will see that BWTC is not merely a building but a declaration of architectural creativity.